About
- “RG” refers to “Radio Guide”, originally a unit indicator for bulk RF cable in the U.S. military’s Joint Electronics Type Designation System.
Usage:
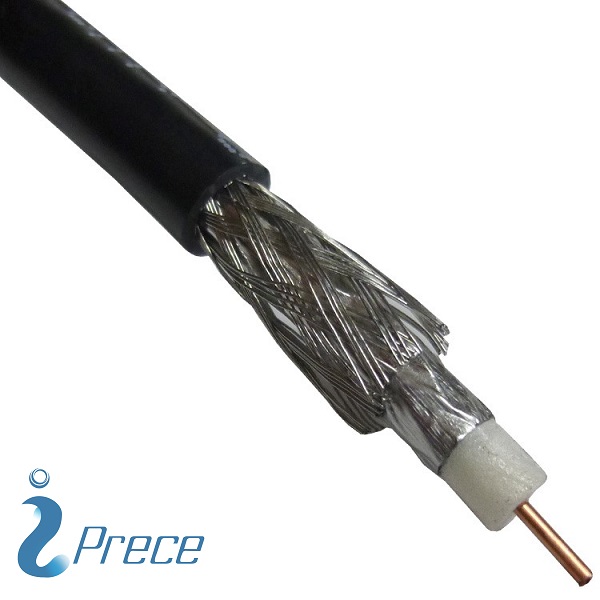
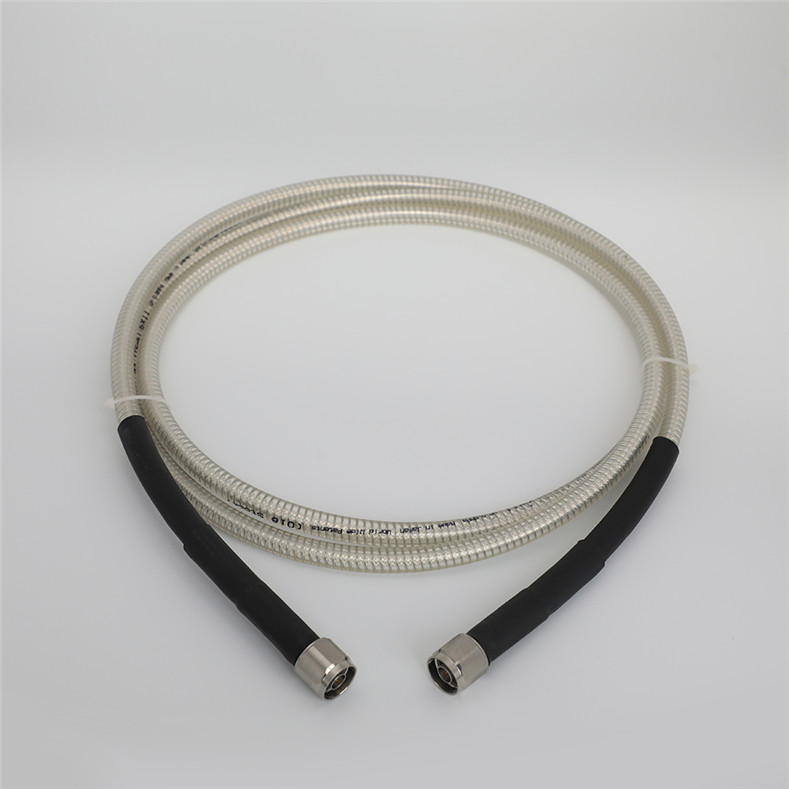
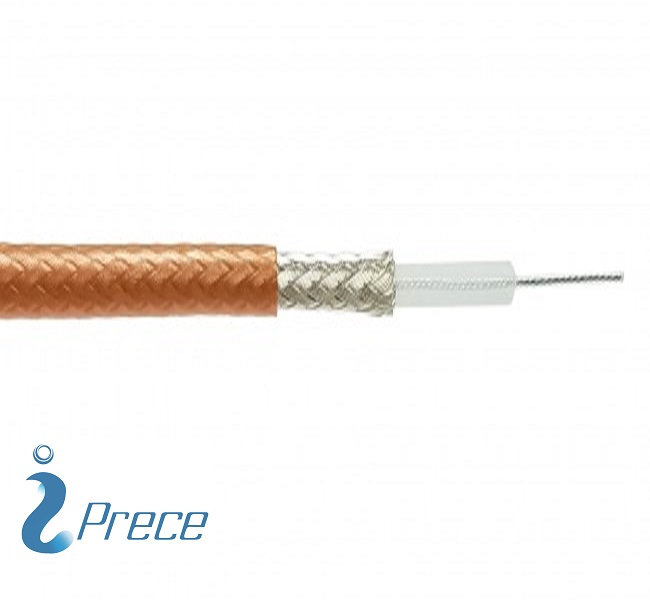
- RG11 Coaxial Cables are used for Wide Broadband with far signal transmission distance, often used as a main cable line in transmitting observing camera data, Cable Television, etc.
Difference Between RG6 and RG11
- RG11 is better at preserving signal quality than the RG6
- RG11 is able to work at much higher frequencies than the RG6
- RG11 costs more than RG6
- RG11 is twice as thick as RG6
- RG11 is not as flexible as RG6
- We can use RG11 to replace RG6
Comparison Chart
| Categories |
RG6 |
RG11 |
| Uses |
Mostly used for satellite cables |
Only reserved for special uses |
| Price |
Less expensive |
More expensive |
| Thickness |
0.375 inches or ⅜ inches |
0.75 inches or ¾ inches |
| Flexibility |
More flexible and less stiff |
Less flexible and stiffer |
| Attenuation |
More signal loss |
Less signal loss |
| Center Conductor |
18AWG |
14AWG |
See All RG Series Coaxial Cables here























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.