About
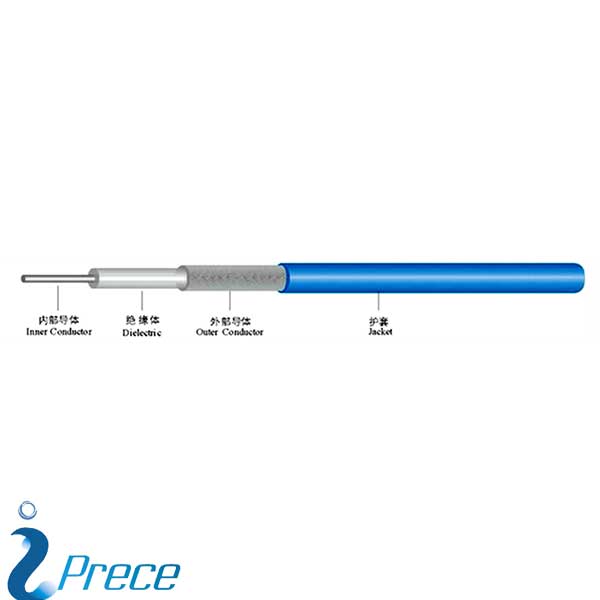
- “RG” refers to “Radio Guide”, originally a unit indicator for bulk RF cable in the U.S. military’s Joint Electronics Type Designation System.
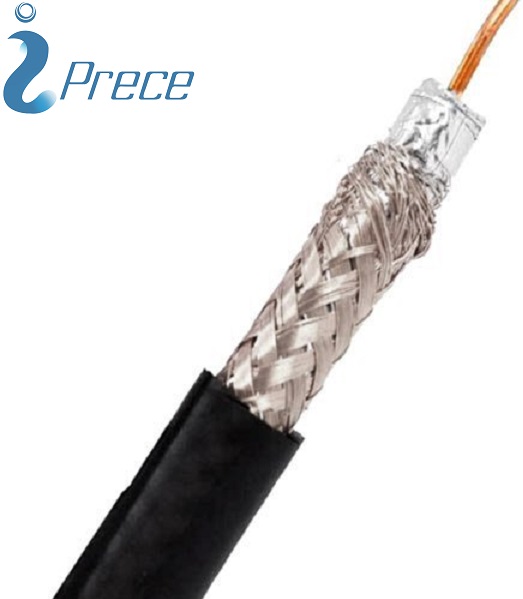
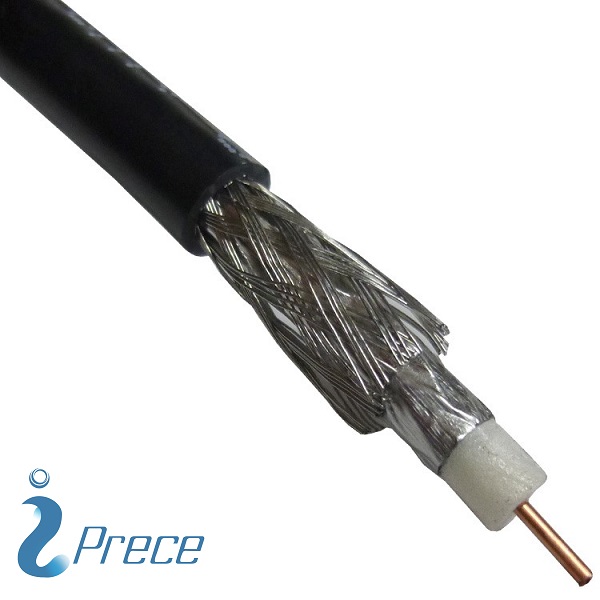
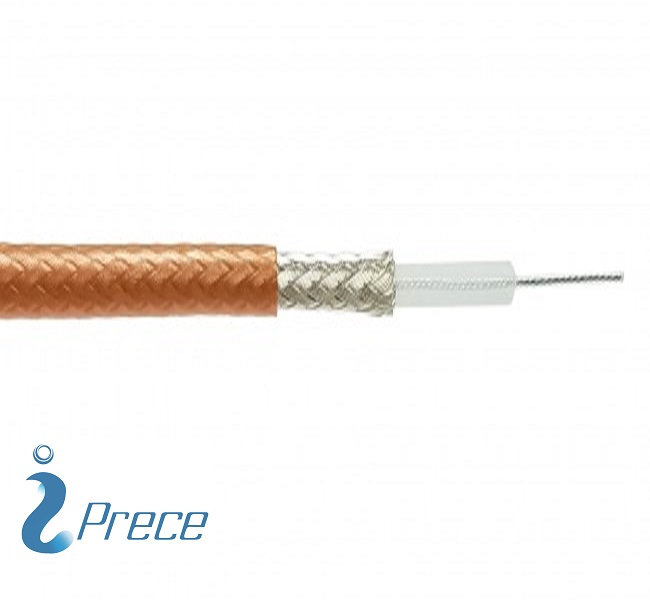
- RG-59/U is a specific type of coaxial cable that is usually used for low-power video and RF signal connections.
- The cable has a characteristic impedance of 75 ohms.
- RG-59 is often used at baseband video frequencies, such as composite video. It may also be used for broadcast frequencies, but its high-frequency losses are too high to allow its use over long distances; in these applications, RG-6 or RG-11 is used instead.
- RG-59 coaxial cable is commonly packed with consumer equipment, such as VCRs or digital cable/satellite receivers. Manufacturers tend to include only RG-59 cables because it costs less than RG-6. However, given the short lengths provided (usually 4–6 ft or 1.2–1.8 m), this is generally sufficient for its typical use.
Usage:
- RG-59 is often used at baseband video frequencies, such as composite video. It may also be used for broadcast frequencies, but its high-frequency losses are too high to allow its use over long distances; in these applications, RG-6 or RG-11 is used instead.
- RG-59 is an excellent cable synchronize two digital audio devices, such as ADAT optical devices.
The differences among RG6 and RG59
- RG59 cable has been around for a long time. This cable used to be what most people used for their cable TV connection and is very commonly installed in older homes and commercial buildings. However, many modern signal requirements have made this cable less popular in the last few years. RG 59 has a smaller conductor than RG 6, which means that it can’t achieve the same signal quality as RG 6. The way its shielding is designed also means that it doesn’t keep Gigahertz level signals inside the conductor very well. This is why RG 59 probably isn’t a good choice for your TV or internet connection.
- RG6 Coaxial Cables are used for Base band with near signal transmission distance, often used as a cable branch to transmit observing camera data and connect Indoor Television Equipment.
- RG 6 is recommended for your CATV, satellite, TV antenna, or broadband internet. RG 59 is generally better for most CCTV systems and other analog video signals. What you really need to consider are the frequency ratings your equipment uses. If your equipment uses higher frequencies (above 50 MHz), then you’ll want to go with RG 6. If your frequencies are lower than that, then you’ll want to use RG 59.
- RG6 can transmit signals in a higher frequency range than RG6.
RG 59 Signal Loss (in dB) per 100 ft
- Loss at 50 MHz: 2.4 dB
- Loss at 100 MHz: 3.4 dB
- Loss at 400 MHz: 7.0 dB
- Loss at 900 MHz: 11.1 dB
- Loss at 1000 MHz: 12.0 dB
RG 6 Signal Loss (in dB) per 100 ft
- Loss at 50 MHz: 1.5 dB
- Loss at 100 MHz: 2.0 dB
- Loss at 400 MHz: 4.3 dB
- Loss at 900 MHz: 6.8 dB
- Loss at 1000 MHz: 7.0 dB
We carry a variety of RG59 Coax Connectors, including RCA, BNC, and F-type connectors for the dual and quad shield, as well as twist-on and compression connectors. Factors that may include your choice may include how robust the connection is intended to be, what the application is, and personal preference.
Key Specifications
| Name | RG59 |
| Flex Type | Flexible |
| Impedance | 75 Ohm |
| Dielectric Type | PE |
| Jacket Diameter | 0.774 cm |
| Jacket Material | PVC |
| Number of Shields | 2 |
| Attenuation at 1 GHz | 9.2 dB |
| Max Power at 1 GHz | 52 Watts |
| Max Frequency | 1 GHZ |
| Max Operating Temperature | 80℃ |
| Center Conductor Type | Solid |
| Inner Conductor, Number of Strands | 1 |
| Coax Type | Coax |























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.